What Is Cervix? Understanding the Role of Cervix in Women's Health
What is cervix?
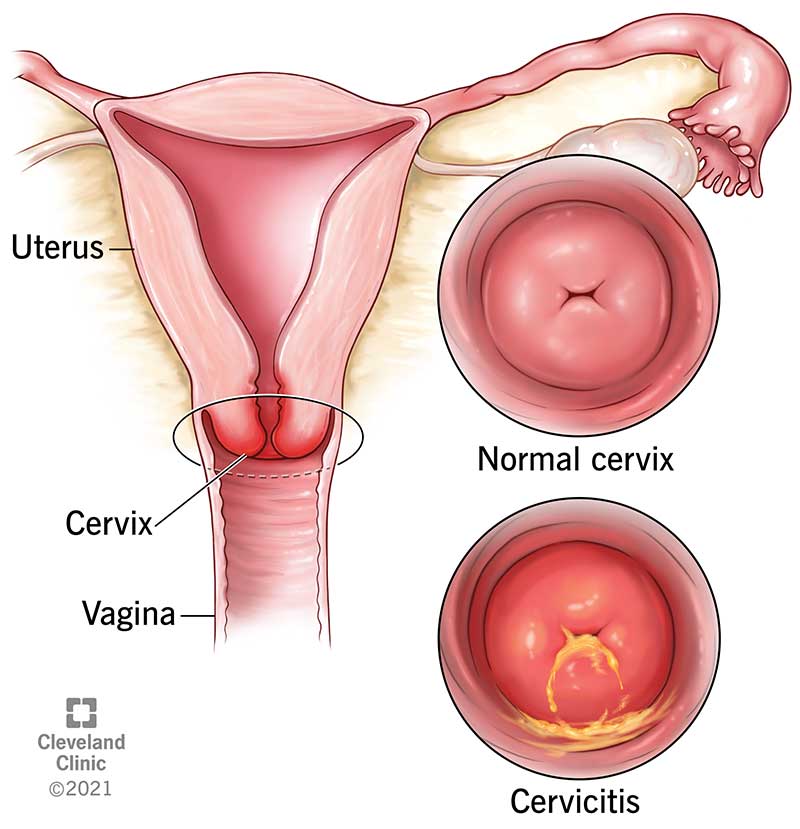
The cervix is a vital part of the female reproductive system, yet it often goes unnoticed until something goes wrong. The cervix is a small, cylindrical-shaped organ that connects the uterus to the vagina. It plays a crucial role in fertility, menstrual cycles, and childbirth. Understanding what the cervix is, its anatomy, and how it functions is essential for women's reproductive health.
In this article, we will explore the cervix in more detail, including its anatomy, function, and importance in women's health. We will also discuss the common issues related to the cervix, such as cervical cancer, and how to maintain a healthy cervix.
Anatomy of the Cervix
The cervix is located at the lower end of the uterus and protrudes into the vagina. It is made up of two main parts, the endocervix and the ectocervix. The endocervix is the inner part of the cervix that lines the cervical canal and produces mucus that helps sperm move through the cervix and into the uterus. The ectocervix is the outer part of the cervix that is visible from the vagina.
The cervix has an opening, called the cervical os, which changes in size and shape during a woman's menstrual cycle. During ovulation, the cervical os opens to allow sperm to enter the uterus and fertilize an egg. After ovulation, the cervical os closes, forming a mucus plug to prevent bacteria from entering the uterus.
Function of the Cervix
The cervix plays a crucial role in women's reproductive health. It not only serves as a pathway for sperm to enter the uterus but also acts as a barrier to prevent harmful bacteria from entering the uterus. The cervix produces mucus that changes in consistency throughout a woman's menstrual cycle to aid in fertility. The mucus becomes thinner and more alkaline around ovulation, making it easier for sperm to swim through the cervix.
During childbirth, the cervix dilates or opens to allow the baby to pass from the uterus into the birth canal. The cervix can dilate up to ten centimeters during labor, allowing the baby to pass through. After childbirth, the cervix returns to its normal size and shape.
Importance of Cervical Health
Maintaining cervical health is essential for women's overall reproductive health. Cervical cancer is a common type of cancer that affects the cervix. According to the American Cancer Society, an estimated 14,480 new cases of invasive cervical cancer will be diagnosed in 2022 in the United States alone. Regular cervical cancer screenings can detect abnormal cells early, allowing for prompt treatment and a higher chance of successful treatment.
In addition to cervical cancer, other conditions can affect the cervix, such as cervical dysplasia, cervical polyps, and cervicitis. Regular gynecological exams can help detect any issues with the cervix early on and allow for prompt treatment.
Maintaining a Healthy Cervix
Maintaining a healthy cervix is essential for women's reproductive health. There are several steps women can take to ensure their cervix stays healthy, including:
Practice safe sex - Using condoms can help prevent sexually transmitted infections that can lead to cervical cancer.
Get regular cervical cancer screenings - Pap smears or HPV tests can detect abnormal cells early and allow for prompt treatment.
Quit smoking - Smoking can increase the risk of cervical cancer and other reproductive health issues.
Practice good hygiene - Maintaining good hygiene, such as regularly washing the genital area, can help prevent infections that can affect the cervix.
Stay up to date on vaccinations - Getting vaccinated against HPV can reduce the risk of developing cervical cancer.
Eat a healthy diet - A diet rich in fruits and vegetables can help boost the immune system and reduce the risk of cervical cancer.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How often should I get a cervical cancer screening?
The frequency of cervical cancer screenings depends on several factors, including age, medical history, and risk factors. Generally, women between the ages of 21 and 29 should get a Pap smear every three years, while women between the ages of 30 and 65 should get a Pap smear every three to five years or an HPV test every five years.
Can I still get cervical cancer if I've had the HPV vaccine?
While the HPV vaccine can significantly reduce the risk of developing cervical cancer, it does not provide complete protection. Women who have been vaccinated should still get regular cervical cancer screenings to detect any abnormal cells early.
Can pregnancy affect the cervix?
During pregnancy, the cervix may soften and thin out in preparation for childbirth. This is known as effacement and dilation. However, premature effacement and dilation can increase the risk of preterm labor and delivery.
Conclusion
The cervix plays a crucial role in women's reproductive health, and understanding what it is, how it functions, and how to maintain its health is essential. Regular cervical cancer screenings, practicing safe sex, and maintaining good hygiene can help prevent cervical cancer and other conditions that can affect the cervix. By taking proactive steps to maintain cervical health, women can enjoy optimal reproductive health and well-being.
BUY FERTILITY TRACKER
Comments